SOON AVAILABLE
Optical Tweezers can be used for studying mechanical properties of molecules, soft matter, tissues or cells
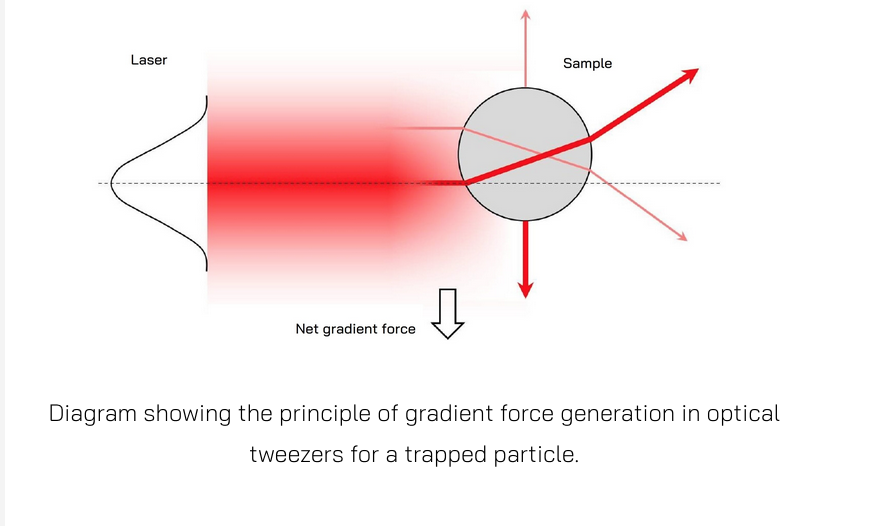
Optical tweezers make use of highly focused laser beams that can trap and manipulate microscopic particles, such as beads, biological cells, and even molecules. Optical tweezers operate based on the principles of light momentum transfer. When a laser beam is focused through a high numerical aperture (NA) lens, it creates a strong electric field gradient. This gradient exerts a force on dielectric particles, drawing them towards the region of highest intensity, typically the focal point of the laser beam.This technique can be applied to perform reology fields, particularly biology and physics. Learn more about optical traps on the Optical Trap Tutorial website
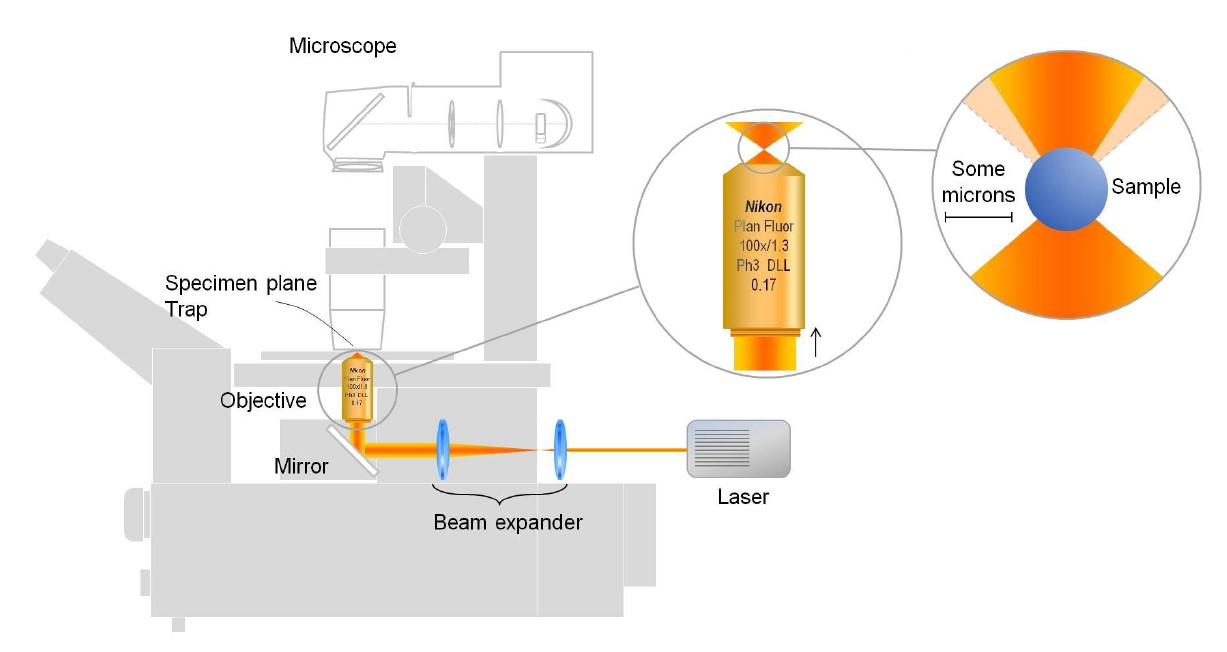
The Impetux Optical Trap is available on the Nikon X-light V3-01 Spinning disk and needs to booked as in PPMS
Optical Trap Specifications:
 Trapping-laser: 5W, 1064nm infrared laser (Laser Safety Class 4).
Trapping-laser: 5W, 1064nm infrared laser (Laser Safety Class 4).
- up to 256 optical traps
- Versatile manipulation options: Trajectories, oscillations, pattern morphing
Optical Trap Applications:
- Trapping-laser: 5W, 1064nm infrared laser (Laser Safety Class 4).
- up to 256 optical traps
- Optimized optical design for an excellent optical trapping efficiency.
- Versatile manipulation options: Trajectories, oscillations, pattern morphing
Optical Tweezers force spectroscopy sensor
 The Optical Tweezers force spectroscopy sensor based on light momentum analysis, and allows direct – calibration free- force measurements on on irregular & non-spherical objects. A force spectroscopy method independent of sample & medium properties
The Optical Tweezers force spectroscopy sensor based on light momentum analysis, and allows direct – calibration free- force measurements on on irregular & non-spherical objects. A force spectroscopy method independent of sample & medium properties
Specifications:
- Direct force measurements: no calibrations needed.
- Simultaneous force measurements for multiple independent traps.
- High Numerical-Aperture (NA=1.4) immersion optics. Optical design optimized for λ=1064 nm.
- Maximum laser power at the sample: 300 mW.
- Force resolution <50 fN.
- Position resolution: 1 nm (typ.).
- Up to 100 kHz, 18-bit, analog-to-digital conversion.
